Understanding Uniform Rectilinear Motion: Concepts and Equations
Classified in Physics
Written on in  English with a size of 4.39 KB
English with a size of 4.39 KB
Uniform Rectilinear Motion
A rectilinear movement is when an object is described as moving in a straight path, and is uniform when its speed is constant over time, as its acceleration is zero. We refer to it by the acronym MRU.
The MRU is characterized by:
- Movement is done on a straight line.
- Velocity is constant, involving constant magnitude and direction.
- The magnitude of velocity is called speed.
- Zero acceleration.
Kinematics (Greek κίνημα, Kine, movement) is the branch of classical mechanics that studies the laws of motion of bodies without regard to the causes that produce it, limited essentially to the study of time-dependent trajectory.
Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion
In this motion, the acceleration is constant, so the mobile speed and position vary linearly with time quadratically. The equations governing this motion are:


Free-fall is the motion of a body under the exclusive action of a gravitational field. Although this formal definition excludes the influence of other forces such as aerodynamic drag, often they must be taken into account when the phenomenon occurs within a fluid, like air or other fluid. The concept is applicable even to moving objects upwardly decelerating under the action of gravity.
Equation of Motion
By Newton's second law, force  acting on a body equals the product of its mass
acting on a body equals the product of its mass  by the acceleration it acquires. In free fall involving only the weight
by the acceleration it acquires. In free fall involving only the weight 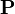 (vertically downwards) and the aerodynamic drag
(vertically downwards) and the aerodynamic drag 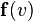 in the same direction, and opposite to the velocity. Within an approximately constant gravitational field, the equation of motion of free fall is:
in the same direction, and opposite to the velocity. Within an approximately constant gravitational field, the equation of motion of free fall is:

|
|
