Understanding Data Storage and Binary Number Representation
Classified in Computers
Written on in  English with a size of 221.76 KB
English with a size of 221.76 KB
Data Storage Conversion:
- 1 gigabyte (GB) equals 1,024 megabytes (MB).
- 1 megabyte (MB) equals 1,024 kilobytes (KB).
- To convert gigabytes to kilobytes, multiply by 1,024 twice. For example: 1 GB = 1,024 MB * 1,024 KB = 1,048,576 KB.
- To convert gigabytes to megabytes, multiply by 1,024. For example: 1 GB = 1,024 MB
- To convert 20 megabytes to bytes: 20 MB = 20 * 1,024 KB * 1,024 bytes = 20,971,520 bytes
- To convert 2 gigabytes to kilobytes: 2 GB = 2 * 1,024 MB * 1,024 KB = 2,097,152 KB
Example: SHKRONJA A has a value of 1010, B - 1011, C - 1100, D - 1101, E - 1110, F - 1111.
Binary Number Representations
There are three main ways to represent signed numbers in binary:
1. Signed Magnitude
- Positive Numbers: Standard binary representation.
- Negative Numbers: The leftmost bit (most significant bit) is the sign bit (0 for positive, 1 for negative). The remaining bits represent the magnitude.
- Example: +7: 0000111; -7: 1000111
2. One's Complement
- Positive Numbers: Standard binary representation.
- Negative Numbers: The leftmost bit is the sign bit. To find the one's complement of a negative number, flip all the bits.
- Example: +7: 0000111; -7: 1111000
3. Two's Complement
- Positive Numbers: Standard binary representation.
- Negative Numbers: The leftmost bit is the sign bit. To find the two's complement, find the one's complement and add 1.
- Example: +7: 0000111; -7: 1111001 (one's complement: 1111000 + 1 = 1111001)
Key Point
In all three representations, the leftmost bit indicates the sign (0 for positive, 1 for negative), and the remaining bits represent the magnitude. Each bit position has a weight based on powers of 2.
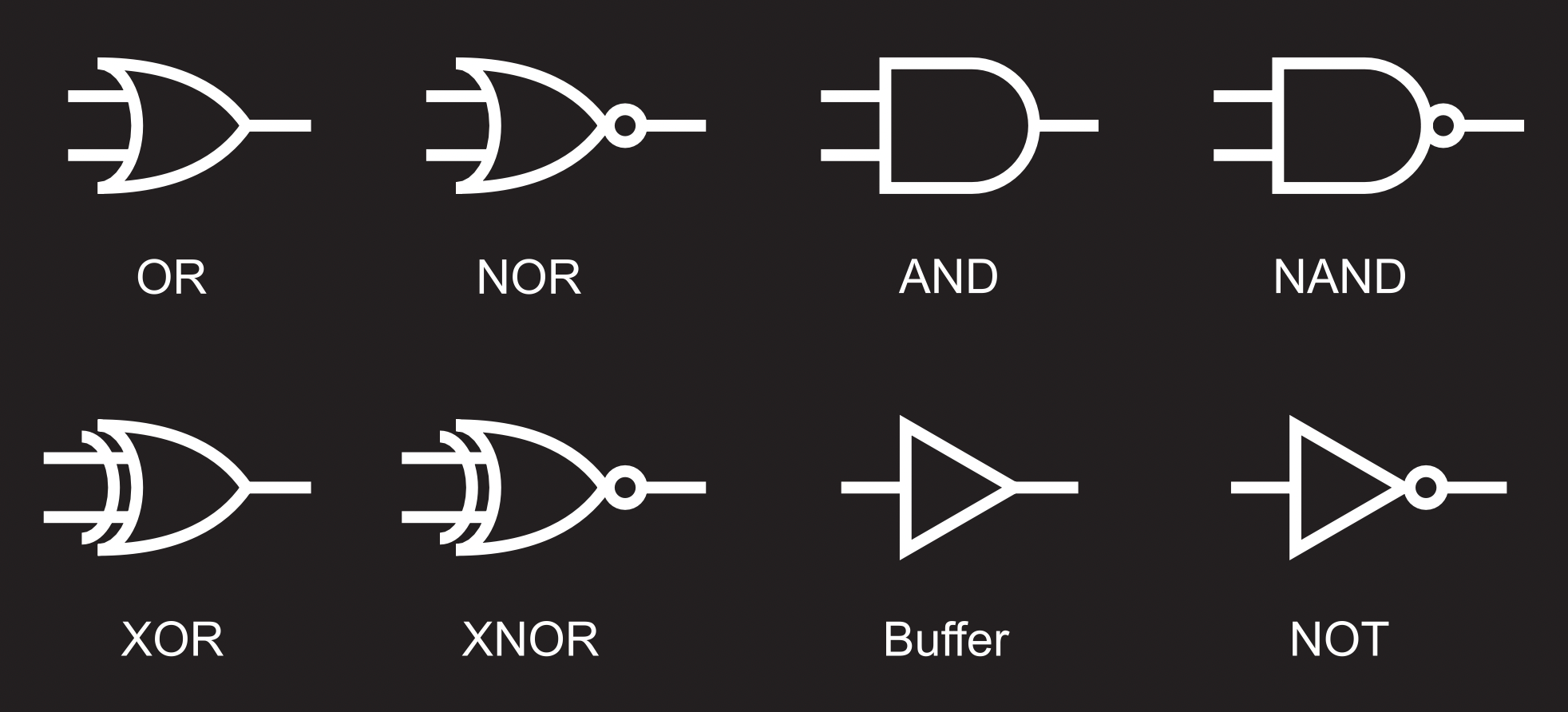
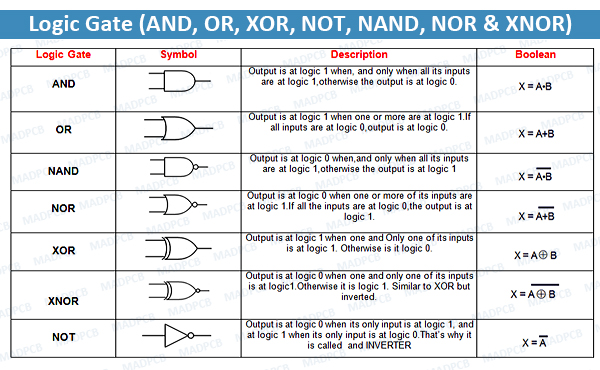
DeMorgan's Law Example
Using DeMorgan's Law, write an expression for the complement of F if F(w,x,y,z) = xz'(x'yz + x) + y(w'z + x').
Answer:
F(w,x,y,z) = xz'(x'yz + x) + y(w'z + x')
F'(w,x,y,z) = (xz'(x'yz + x) + y(w'z + x'))'
= (xz'(x'yz + x))'(y(w'z + x'))'
= ((xz')'+(x'yz + x)')(y'+(w'z + x')')
= ((x'+z)+(x+y'+z')(x'))(y'+((w+z')(x))
< >
>
< >
>
<
> <
>
<
>
