Understanding Current Density and Electromotive Force
Classified in Physics
Written on in  English with a size of 2.16 KB
English with a size of 2.16 KB
Current Density
The electric current density is a vector quantity representing power per unit area. It relates to current as:

- I is the electric current in amperes (A).
- j is the current density in amperes per square meter (Am-2).
- S is the area in square meters (m²).
Isolated Point Charges
Current density relates to charge carriers (electrons, holes, ions) by:

Where:
- ni is the concentration of carrier i.
- qi is the electric charge of carrier i.
- vi is the average velocity of carrier i in the volume.
Electromotive Force (EMF)
Electromotive force maintains a potential difference in an open circuit or produces current in a closed circuit. It's a generator characteristic, explained by an electric field Ξ, where  defines the EMF.
defines the EMF.
EMF is the work done to move a unit positive charge from negative to positive inside the generator, measured in volts (V).

It relates to potential difference V and internal resistance r by: E = V + Ir. (Ir is the potential drop inside the generator due to resistance).
The induced EMF in a closed circuit equals the rate of change of magnetic flux Φ: 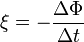 (Faraday's Law). The negative sign (Lenz's Law) indicates the induced EMF opposes the flux change.
(Faraday's Law). The negative sign (Lenz's Law) indicates the induced EMF opposes the flux change.
