Core Web Development Concepts: Languages, Protocols, and Frameworks
JavaScript: The Heart of Interactive Web Development
JavaScript is a powerful and widely used programming language mainly used for making websites interactive and dynamic. It works on the client-side, which means it runs inside the user's web browser. JavaScript allows web pages to respond to user actions like clicking buttons, typing in text boxes, hovering over images, and more. It works together with HTML (for structure) and CSS (for design) to build modern and user-friendly websites. It is easy to learn and used by almost every website today.
Apart from the client-side, JavaScript is also used on the server-side using platforms like Node.js, which allows building full web applications using JavaScript alone. It is a platform-independent language, meaning it can work on any operating system or browser. JavaScript also supports features like object-oriented programming, event handling, and asynchronous programming, which makes it fast and flexible for developers. That’s why JavaScript is called the heart of modern web development.
Main Features of JavaScript:
- Lightweight: Simple and fast scripting language.
- Interpreted Language: No compilation needed; runs directly in the browser.
- Object-Oriented: Supports objects, properties, and methods.
- Event Handling: Responds to user actions (clicks, scrolls, etc.).
- Client-Side Execution: Runs in the user’s browser, reducing server load.
- Platform Independent: Works across all browsers and devices (Windows, Mac, Linux, etc.).
Understanding PHP and Its Data Types
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a server-side scripting language designed to develop dynamic and interactive web applications. It is easy to use, open-source, and works well with databases like MySQL. PHP is embedded inside HTML and is executed on the server, and the result is sent to the user’s browser.
PHP supports many data types, which are used to store values:
- Integer: Whole numbers (e.g., 10, -5)
- Float (Double): Decimal numbers (e.g., 4.5)
- String: Sequence of characters (e.g., "Hello")
- Boolean: True or False
- Array: Collection of multiple values in one variable
- Object: Instances of user-defined classes
- NULL: Represents no value
PHP is widely used in login systems, online forms, shopping carts, and more. It is flexible, fast, and works on all platforms.
CSS: Styling Web Pages with Cascading Style Sheets
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is used to control the design and layout of web pages. While HTML is used to create the structure of a webpage (like headings, paragraphs, buttons), CSS is used to style those elements — like setting colors, fonts, spacing, alignment, and animations. It helps in making the webpage look attractive and professional.
CSS is important because it separates design from content. Instead of writing style in every HTML tag, we can write CSS once and apply it to multiple pages or elements. This makes the website easy to maintain and update. CSS is supported by all modern browsers and can be used to design for different devices like phones, tablets, and desktops using responsive design.
Types of CSS:
- Inline CSS: Written directly inside the HTML tag using the
styleattribute.
Example:<p style="color: red;">Hello</p> - Internal CSS: Written inside a
<style></style>tag in the HTML file’s<head>section.
Example:<style> p{color:blue}</style> - External CSS: Written in a separate
.cssfile and linked to the HTML page.
Example:<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
Advantages of CSS:
- Separation of Content and Design: Makes the code cleaner and easier to manage.
- Reusability: One CSS file can be used for multiple HTML pages.
- Faster Page Loading: Reduces HTML file size by removing repeated styling.
- Consistency: Keeps design uniform across all web pages.
- Responsive Design: CSS can adapt the website for mobile, tablet, or desktop screens.
- Easy Maintenance: Change the design in one place and it updates everywhere.
DOM: The Document Object Model Explained
DOM stands for Document Object Model.
It is a tree-like structure that represents the content of a web page in the browser.
When a web page is loaded, the browser converts the HTML into a DOM. This allows JavaScript to read, change, add, or delete any part of the web page dynamically.
DOM treats every part of an HTML page (like elements, attributes, and text) as objects or nodes. These nodes are arranged in a hierarchy (parent-child structure), which makes it easy to access and update parts of the page using JavaScript.
Structure / Levels of DOM:
DOM is like a family tree with different levels. Here’s how it looks:
Levels in DOM:
- Document Node: Topmost node (whole HTML document).
- Element Nodes: HTML tags like
<html>,<body>,<p>, etc. - Attribute Nodes: Attributes like
id,class,styleinside elements. - Text Nodes: The actual text inside elements.
Example: <h1>Hello</h1>
DOM Tree for above:
Document
└── html
└── body
└── h1
└── "Hello"Use of DOM:
- Change content (
document.getElementById().innerHTML) - Change styles (
element.style.color = "red") - Add or delete elements dynamically
Understanding XML: Extensible Markup Language
XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. It is a markup language mainly used to store and transport data in a structured format. Unlike HTML, which is used to display data on web pages, XML focuses on what the data is rather than how it looks. It allows users to create their own custom tags based on the type of data they want to store. For example, you can use <name></name>, <age></age>, or <student></student> as tags to represent your data. XML is both human-readable and machine-readable, which makes it easy to share data between different platforms, software, or systems.
One of the key features of XML is that it separates data from presentation, meaning the data can be stored independently from how it is displayed. This is useful in web applications, software development, and mobile apps. XML is also platform-independent and supports Unicode, so it can store data in any language. Because of its tree-like structure, XML is easy to organize and manage. It is widely used in areas like web services (SOAP), configuration files, Android development, and data exchange between systems.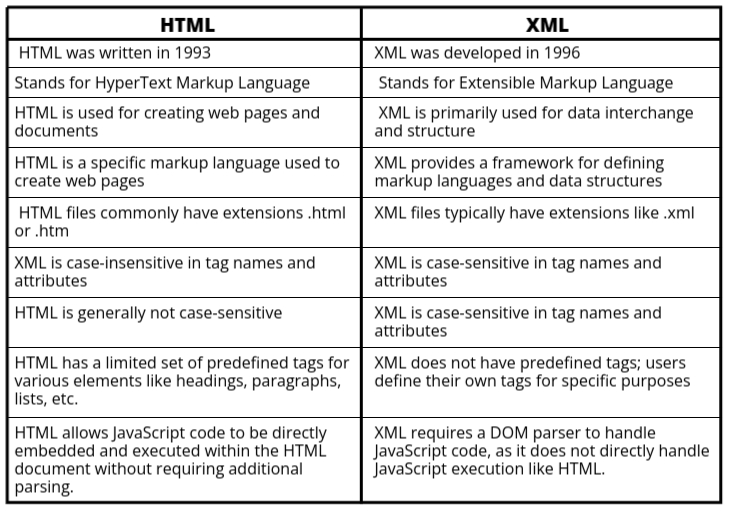
Java Servlets: Building Dynamic Web Applications
A Servlet is a Java program that runs on a web server and is used to create dynamic web pages. It acts like a middle layer between the browser (client) and the database (server). When a user sends a request from a web page (like submitting a form), the servlet receives it, processes it (e.g., stores data or fetches data from a database), and then sends back a response, usually in HTML format. Servlets are part of Java EE (Enterprise Edition) and are managed by a Servlet container like Apache Tomcat.
Servlets are used to build powerful, secure, and fast web applications. They support features like session management, cookies, and database connectivity. Servlets are written entirely in Java, so they are platform-independent, scalable, and object-oriented. They are more efficient than traditional CGI scripts because they don’t create a new process for each request — they use threads, which are faster. Servlets are commonly used in login systems, online forms, shopping carts, and more.
Servlet Lifecycle Methods:
init()Method: This method is called only once when the servlet is first loaded into memory. It is used to initialize resources like database connections or configuration settings.service()Method: This method is called every time a client sends a request. It contains the main logic to process requests and send responses (like displaying data, processing forms, etc.). It automatically callsdoGet(),doPost(), etc. based on the request type.destroy()Method: This method is called only once when the servlet is removed from memory or the server shuts down. It is used to release resources like closing files or database connections.
Server Starts
↓
init() → called once
↓
service() → called for every request
↓
destroy() → called once before servlet is removed
Struts Framework and MVC Architecture
Struts is an open-source Java web application framework that is used to create dynamic, enterprise-level web applications. It follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern, which separates the application into three parts: Model (business logic), View (user interface), and Controller (flow control). Struts helps developers build organized, maintainable, and scalable Java web applications by clearly separating the design and code parts.
How Struts Works:
In Struts, when a user sends a request (like submitting a form), the Controller (ActionServlet) receives it and sends it to the appropriate Model (Java class) for processing. Once the processing is done, the result is passed to the View (usually a JSP page) to display the output to the user. Struts uses configuration files (like struts-config.xml) to map user actions to specific classes and pages. This framework reduces coding effort, improves structure, and allows faster development of complex web applications.
MVC Architecture in Struts:
- The Model contains the application logic and communicates with the database.
- The View is the user interface (usually JSP pages).
- The Controller handles the user input and coordinates between the view and model.
In Struts, when a user sends a request (like submitting a form), it goes to the Controller (ActionServlet), which processes it using Action classes (Model), then forwards the result to a JSP page (View). This clear separation improves performance, maintainability, and reusability.

Connecting PHP to MySQL with MySQLi
To connect PHP with a MySQL database, we use the MySQLi (MySQL improved) extension. It allows us to connect to the database, run SQL queries, and fetch data. First, we establish a connection using mysqli_connect(), then we write a SELECT query to get data from the table, and finally use mysqli_fetch_assoc() or mysqli_fetch_array() to display that data in a loop.
We usually use tables like students, users, or products in our database. After getting the data, we can display it using HTML and PHP echo.
<?php
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($host, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT * FROM students";
// 3. Run query and get result
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
// 4. Display data in table
if (mysqli_num_rows($result) > 0) {
echo "<table border='1'>";
echo "<tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th><th>Email</th></tr>";
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>".$row['id']."</td>";
echo "<td>".$row['name']."</td>";
echo "<td>".$row['email']."</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
} else {
echo "No records found.";
}
// 5. Close connection
mysqli_close($conn);
?>JavaServer Pages (JSP): Dynamic Web Content
JSP (JavaServer Pages) is a server-side technology used to create dynamic web pages using Java. It allows us to embed Java code directly into HTML pages, which makes it easy to build web applications that can interact with databases, take user input, and display real-time data. JSP is a part of Java EE (Enterprise Edition) and runs on a web server like Apache Tomcat. When a JSP page is requested, the server translates it into a Java Servlet behind the scenes and then executes it.
The main advantage of JSP is that it separates the presentation (HTML) from the logic (Java code). This makes web applications easier to manage and update. JSP supports built-in tags, JavaBeans, and custom tag libraries, which help in reducing code complexity. Developers use JSP to create login pages, display database records, and handle user input. Since JSP is Java-based, it is platform-independent, secure, and scalable — suitable for both small and large web applications.
JSP Program to Display Current Date and Time:
<html>
<head>
<title>Current Date and Time</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Current Date and Time:</h2>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" %>
<%
Date currentDate = new Date();
// Display current date and time
out.println("Current Date and Time is: " + currentDate.toString());
%>
</body>
</html>OUTPUT:
Current Date and Time is: Wed Jul 03 23:15:52 IST 2025
Explanation:
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" %>: Imports the Date class from Java.Date currentDate = new Date();: Creates an object that holds the current system date and time.out.println(...): Prints the date and time on the browser using JSP's output stream.
jQuery: Simplifying JavaScript for Web Development
jQuery is a lightweight JavaScript library that makes it easier to use JavaScript on a website. It helps to perform common web tasks like DOM manipulation, event handling, animations, and AJAX calls in fewer lines of code. jQuery is simple to learn and reduces the amount of JavaScript code needed for dynamic features.
One of the best features of jQuery is that it works across all browsers (cross-browser compatible). It uses a very simple syntax: for example, to select an element and hide it, we just write $("#id").hide();. jQuery also supports animations, effects, and handling user actions like clicks, form input, etc.
AngularJS: Building Dynamic Single-Page Applications
AngularJS is an open-source JavaScript framework developed by Google. It is used to build dynamic, single-page web applications (SPAs). AngularJS extends HTML with additional custom tags and attributes called directives, and it adds data binding and dependency injection, making web development faster and easier. It is based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which helps separate the application logic, data, and user interface.
AngularJS uses two-way data binding, which means that any change in the user interface automatically updates the data in the model and vice versa. It also supports form validation, filters, custom directives, and reusable components. Developers use AngularJS to create dynamic web forms, dashboards, and real-time applications without reloading the page. Since it runs in the browser, it reduces the load on the server and improves the user experience.
Understanding the World Wide Web (WWW)
WWW stands for World Wide Web. It is a system of interlinked web pages and multimedia content that can be accessed using the Internet. It uses browsers (like Chrome, Firefox) to view websites. The WWW works through protocols like HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), which helps in communication between web browsers (clients) and web servers.
When you type a URL (like www.google.com) into a browser, it sends a request to the server, and the server sends back a web page. This process is made possible by the World Wide Web. It includes everything like websites, videos, images, text, and documents that are connected and accessible online.
HTTP: Request and Response Protocol
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the protocol used to transfer data between the browser and the web server. It works using two main parts: request message and response message.
HTTP Request Message:
This is sent from the client (browser) to the server. It includes:
- Request line (e.g.,
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1) - Headers (like browser info, cookies)
- Body (optional – used in
POSTrequests to send form data)
HTTP Response Message:
This is sent from the server to the client (browser). It includes:
- Status line (e.g.,
HTTP/1.1 200 OK) - Headers (server info, content type)
- Body (actual content like HTML, image, etc.)
Example Flow:
- Browser sends HTTP request:
GET /home.html - Server responds with:
200 OKand the webpage content
Java Servlet Session Management
In Java Servlets, session management is used to track a user’s data (like login info) across multiple pages during a visit. Since HTTP is stateless, the server doesn’t remember the user between requests. To fix this, servlets use HttpSession to store user data during a session. A session begins when the user accesses the web app and ends when the browser is closed or the session expires.
How HttpSession Works:
Java provides the HttpSession interface to create, read, and remove session data. We can use session.setAttribute() to save data and session.getAttribute() to retrieve it. This is useful for things like user login, shopping carts, or temporary user data.
Session Handling Example:
// Inside your servlet (e.g., LoginServlet)
HttpSession session = request.getSession(); // Create or get session
session.setAttribute("username", "Narayan"); // Store data in session
// Another servlet or page
String user = (String) session.getAttribute("username"); // Read session data
response.getWriter().println("Welcome, " + user);Session Management Methods:
getSession(): Get or create sessionsetAttribute("key", value): Store datagetAttribute("key"): Get datainvalidate(): Destroy session
Interceptors in Java Frameworks
Interceptors are special components used in Java frameworks like Struts2 or Spring to intercept (i.e., stop and check) requests and responses before or after they reach the main program (like an action class or controller). They are like filters, used to perform common tasks such as logging, authentication, input validation, or measuring execution time — without writing the same code again and again.
Interceptors help developers to separate cross-cutting concerns (common tasks) from business logic. For example, if every action in your app needs to check whether the user is logged in or not, instead of writing the login check in every class, you write one interceptor for it — and it runs automatically for all actions.
How Interceptors Work:
In Struts2, when a user makes a request, the request first goes through a stack of interceptors. These interceptors can:
- Do something before the request reaches the Action class.
- Let the Action class handle the request.
- Then do something after the Action class finishes.
The interceptor can allow the request to proceed or stop it (like if the user is not logged in). This process is automatic and defined in the struts.xml file.
PHP Session Management
A session in PHP is a way to store user information (like login data) across multiple pages of a website. Unlike cookies (which store data in the browser), session data is stored on the server, making it more secure. Each user gets a unique session ID, which helps track their activity during their visit to the site.
<?php session_start(); // Start the session // Store session data $_SESSION['username'] = "Narayan"; // To destroy a session (example, typically on logout) // session_destroy(); ?>

 English with a size of 332.62 KB
English with a size of 332.62 KB