Chemical Bonding and Atomic Structure: A Comprehensive Guide
Classified in Chemistry
Written on in  English with a size of 31.21 KB
English with a size of 31.21 KB
Metal + nonmetal = ionic bond
Nonmetal + nonmetal = covalent bond
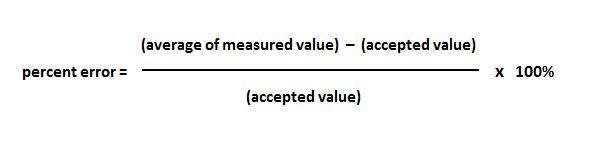
Metal + metal = metallic bond
Electron filling pattern: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f
Physical Changes
- Do not create a new substance.
Chemical Changes - Do produce new substances.
Ions - Atoms can gain or lose electrons to form ions (atoms with a charge.
• Anion - Atom with a negative charge.
• Cation - Atom with a positive charge.
quantitative= number/amount, qualitative= observation of physical change
alkali metals the column of elements from lithium to francium.
Alkaline earths the column of elements from beryllium to radium.
Halogens the column of elements from fluorine to astatine.
The Periodic Law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements recur in a systematic and predictable way when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
Mendeleev arranged the elements to atomic mass
Isotopes are elements with a different amount of neutrons
Atomic mass=Proton and neutrons
The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength
The greater the energy, the larger the frequency
656.2 red 486.1 blue-green 434.0 blue-violet 410.1 violet Ionic Compounds
1. Write the symbol and charge of the cation (metal) first and the anion (nonmetal) second. Al3+N3−Al3+N3− Li+O2−Li+O2− 2. Use a multiplier to make the total charge of the cations and anions equal to each other. total charge of cations = total charge of anions
1(3+) = 1(3-)
+3 = -3
total charge of cations = total charge of anions
2(1+) = 1(2-)
+2 = -2
3. Use the multipliers as subscript for each ion. Al1N1Al1N1 Li2O1Li2O1 4. Write the final formula. Leave out all charges and all subscripts that are 1.
Intensive- mass doesn't matter
SPDF Orbitals:S-1 P-3 D-5 F-7
Shorthand Electron Configuration- Abbreviated electron configuration
Isoelectronic- Same amount of electrons
